Introduction
In 2025, mobile app development is more dynamic and powerful than ever. But with innovation comes risk. As mobile apps handle sensitive user data like financial information, personal identifiers, and health records, security has become the top priority for developers worldwide.
Cybercrime is predicted to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 (source: Cybersecurity Ventures). Mobile apps are prime targets—ranging from phishing and data leaks to malware injection and API vulnerabilities. Whether you’re building an eCommerce platform, a fintech app, or a social media network, the security of your mobile app defines your credibility.
This guide explores the top mobile app security practices for developers in 2025—covering prevention strategies, real-world examples, and the latest technologies to safeguard your apps and users.
The State of Mobile App Security in 2025
As of 2025, there are over 7.5 billion smartphone users globally. With such widespread usage, app developers face enormous responsibility. According to a Veracode report, 76% of mobile applications have at least one security vulnerability, and 25% contain high-risk flaws.
The main causes? Poor encryption, weak authentication, and insecure APIs.
Modern mobile apps must adopt a security-by-design approach—embedding protection throughout the development lifecycle rather than treating it as an afterthought.
Why Mobile App Security Matters
Security isn’t just a technical requirement—it’s a business imperative. A single breach can result in revenue loss, user distrust, and legal consequences.
Key reasons to prioritize security:
- User trust: Secure apps gain higher retention and positive reviews.
- Compliance: Laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA demand robust data protection.
- Brand reputation: A breach can permanently damage brand credibility.
- Financial safety: Prevent fraud and protect payment transactions.
Example:
In 2023, a major fitness app leak exposed over 20 million user records due to unsecured cloud databases—highlighting why encryption and cloud security are vital.
1. Use Secure Coding Practices
Security starts at the code level. Writing secure code ensures vulnerabilities don’t creep into your app.
Best Practices:
- Avoid hardcoding sensitive data (like API keys or passwords).
- Validate all input to prevent SQL injection or buffer overflow attacks.
- Use obfuscation tools to make reverse engineering harder.
- Keep dependencies and libraries up-to-date.
Tip: Implement Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx to automatically detect vulnerabilities in your source code.
2. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption converts user data into unreadable text, ensuring that even if intercepted, it remains secure.
Best Practices:
- Use AES-256 or RSA-2048 encryption standards.
- Encrypt all data both in transit (using HTTPS/TLS 1.3) and at rest (in databases or storage).
- Implement secure key management with hardware security modules (HSMs).
Example:
WhatsApp uses end-to-end encryption to ensure only the sender and recipient can read messages.
External Reference:
Learn about data encryption standards from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): https://www.nist.gov
3. Secure APIs and Backend Systems
APIs are the backbone of modern mobile apps—but they’re also one of the most common attack vectors.
Best Practices for API Security:
- Use OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect for authentication.
- Validate all incoming requests.
- Limit API exposure by using rate limiting and access control.
- Use JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for secure data exchange.
- Never expose API keys in the client-side code.
Example:
In 2024, a popular shopping app’s API flaw exposed personal details of millions of users. A simple token expiration mechanism could have prevented the breach.
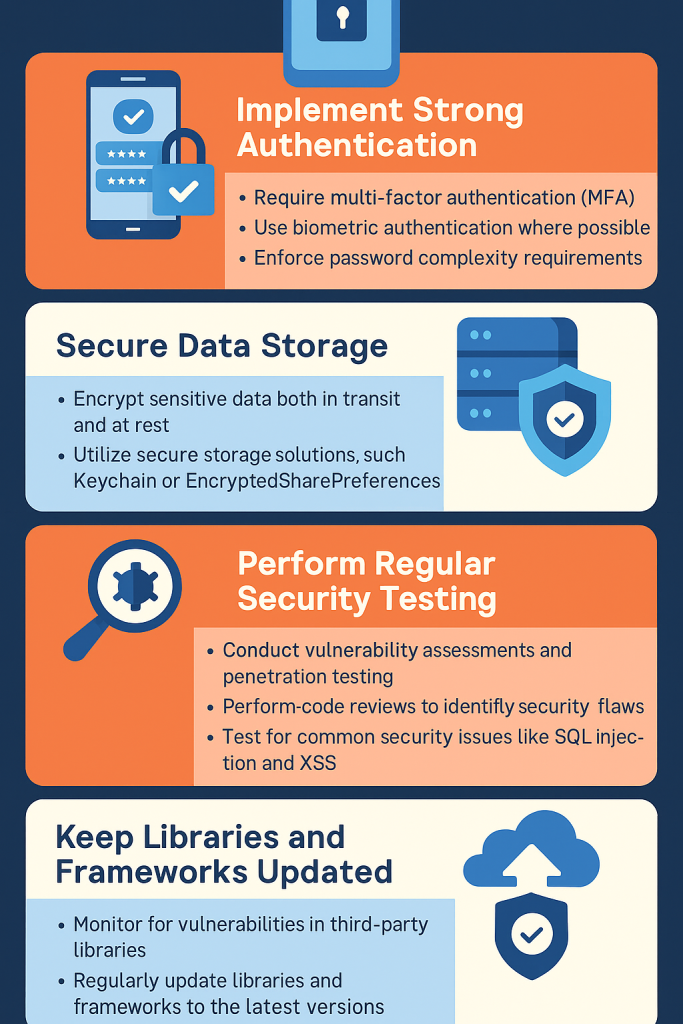
4. Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization
Weak authentication is one of the easiest ways attackers gain access. Multifactor authentication (MFA) is now a standard practice.
Modern Authentication Techniques:
- Biometric authentication: Face ID, fingerprint recognition.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): OTP via SMS or email.
- OAuth and Single Sign-On (SSO): Secure and user-friendly authentication.
Tip: Use zero-trust authentication models, verifying every request regardless of device or network.
Example:
Google Authenticator provides one-time codes that expire quickly, making it difficult for hackers to reuse credentials.
5. Protect Data Storage
Many developers make the mistake of storing sensitive data (like user credentials or session tokens) in plaintext. This can be disastrous if the device is compromised.
Secure Data Storage Tips:
- Use Keychain (iOS) or Keystore (Android) for secure credential storage.
- Avoid storing unnecessary personal information.
- Encrypt shared preferences or local databases.
- Regularly purge cached sensitive data.
Example:
A financial app in 2022 stored tokens in local storage. When a user’s phone was stolen, the attacker accessed account data. Secure storage could have prevented it.
6. Regular Security Testing and Penetration Testing
Continuous testing ensures vulnerabilities are detected before hackers exploit them.
Recommended Testing Methods:
- SAST: Analyze source code for vulnerabilities.
- DAST: Test the running app for real-world exploits.
- Penetration Testing: Simulate attacks to uncover weaknesses.
Tools to Use:
- OWASP ZAP
- Burp Suite
- Metasploit
Reference:
Visit OWASP Mobile Security Project for free testing checklists and resources: https://owasp.org/www-project-mobile-security-testing-guide/
7. Secure Communication with HTTPS and SSL Pinning
Using plain HTTP or insecure communication channels can lead to Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks.
Best Practices:
- Enforce HTTPS using TLS 1.3.
- Implement SSL Pinning to ensure your app connects only to trusted servers.
Example:
Without SSL pinning, attackers can use fake certificates to intercept data. Banking apps like Revolut implement SSL pinning to prevent this.
8. Use Code Obfuscation and App Hardening
Code obfuscation makes it harder for hackers to reverse-engineer your app.
Tools for Code Obfuscation:
- ProGuard (Android)
- R8 for shrinking and optimizing code
- LLVM Obfuscator (iOS)
App Hardening Techniques:
- Disable debugging mode in production.
- Detect rooted/jailbroken devices.
- Use anti-tamper checks.
Example:
Games and fintech apps frequently use code obfuscation to protect against unauthorized access and cloning.
9. Integrate Security in the DevSecOps Pipeline
In 2025, DevSecOps is the standard approach to secure app development. Security is integrated into every stage of the DevOps lifecycle.
Steps to Implement DevSecOps:
- Automate security testing in CI/CD pipelines.
- Train teams on secure coding practices.
- Use AI-based threat detection tools.
Example:
Netflix uses continuous security validation in its DevSecOps process to identify and fix vulnerabilities before release.
10. Keep Dependencies and SDKs Updated
Third-party libraries are often the weakest link in app security. Outdated libraries may contain known vulnerabilities.
Best Practices:
- Audit dependencies using tools like Dependabot or Snyk.
- Use only trusted and verified SDKs.
- Monitor vendor updates regularly.
Example:
A 2024 data breach in a travel app was traced back to a vulnerable analytics SDK that wasn’t updated for months.
11. Implement User Privacy by Design
With growing global privacy regulations, developers must integrate privacy protections from the start.
Privacy Best Practices:
- Ask for only necessary permissions.
- Clearly disclose data collection practices.
- Anonymize user data where possible.
- Allow users to delete their accounts and data easily.
Reference:
Read about GDPR compliance at https://gdpr-info.eu/
Example:
Apple’s iOS apps must now display Privacy Nutrition Labels—summarizing how user data is collected and used.
12. Use AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection
In 2025, AI-driven cybersecurity tools help detect anomalies and respond faster to threats.
Applications of AI in App Security:
- Identifying suspicious login patterns.
- Detecting fraud and malware in real-time.
- Predictive threat intelligence.
Example:
PayPal uses AI algorithms to detect fraudulent activity based on transaction patterns, reducing false positives and improving accuracy.
13. Educate Users About Security
Even the most secure app can be compromised by careless user behavior. Educating users helps prevent breaches.
Tips:
- Add prompts encouraging users to set strong passwords.
- Notify users about app updates.
- Provide security awareness tips in your app’s FAQ section.
Example:
Google Chrome warns users when they enter passwords on insecure websites, promoting safe online behavior.
14. Monitor and Respond to Security Incidents
No system is 100% secure. What matters is how quickly you detect and respond to breaches.
Incident Response Plan:
- Monitor apps using real-time analytics and alerts.
- Establish a clear escalation process.
- Communicate transparently with users during incidents.
- Patch vulnerabilities immediately.
Example:
After a 2023 cyberattack, Zoom rapidly updated its encryption protocols and regained user trust through transparency.
Emerging Mobile Security Trends in 2025
1. Zero-Trust Architecture
Apps no longer trust any device or network by default. Continuous verification ensures tighter security.
2. Decentralized Identity Management
Blockchain-based identity verification reduces data breaches and enhances user privacy.
3. Quantum-Safe Encryption
As quantum computing evolves, developers are adopting encryption resistant to quantum attacks.
4. Edge Security
With more apps leveraging IoT, securing edge devices has become essential.
5. AI-Powered Security Analytics
AI helps analyze millions of data points to detect threats before they occur.
Real-World Example: How a Banking App Secured Its Platform
A major fintech startup in 2024 implemented end-to-end encryption, SSL pinning, and biometric authentication. Within six months:
- Fraud attempts dropped by 70%
- User trust scores improved by 45%
- App store ratings increased from 3.8 to 4.7 stars
This shows how prioritizing security directly impacts business growth.
Conclusion: Security Is the Foundation of App Success
In 2025, app security is not optional—it’s a competitive advantage. Users trust apps that safeguard their privacy and data. Developers who integrate strong security practices early in the development lifecycle build not just safer apps but stronger brands.
By adopting the strategies outlined here—secure coding, encryption, testing, and AI-driven protection—you’ll ensure your mobile app stays resilient against modern cyber threats.
Call to Action
At MobileMerit.com, we help businesses develop secure, scalable, and high-performing mobile apps built for the future. Our expert developers follow the latest security protocols, encryption standards, and DevSecOps practices to ensure your app stays safe from evolving threats.
Ready to build a secure app that users can trust?
Contact MobileMerit.com today for a free mobile app security consultation and learn how we can protect your digital future.
