Introduction: Turning App Ideas into Reality
In the dynamic world of technology, mobile apps have become the driving force behind innovation and customer engagement. By 2025, global app downloads are expected to exceed 260 billion annually (Statista). Whether it’s a startup launching a new idea or an enterprise enhancing digital reach, mobile apps are the bridge between businesses and their customers.
But how exactly does an app evolve from a concept to a fully functional product available on app stores?
That’s where the Mobile App Development Lifecycle (MADL) comes in — a structured process that guides developers through each critical stage of app creation. From initial wireframes to the final deployment, understanding this lifecycle ensures your app is user-friendly, scalable, and market-ready.
In this article, we’ll walk through every phase of the mobile app development lifecycle, share real-world examples, and highlight best practices for success.
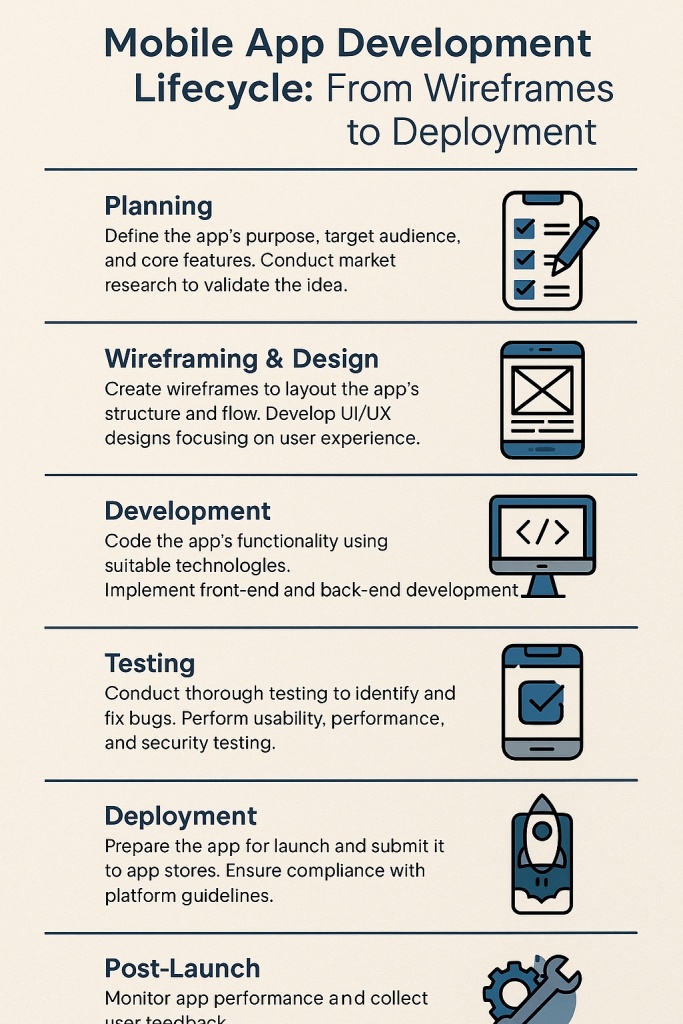
1. Understanding the Mobile App Development Lifecycle
The Mobile App Development Lifecycle (MADL) is a step-by-step framework that outlines the entire process of developing a mobile app — from idea conception to post-launch support.
Key Stages of the Lifecycle:
- Ideation & Research
- Wireframing & Design
- Development (Frontend & Backend)
- Testing & Quality Assurance
- Deployment & Launch
- Maintenance & Updates
Each phase plays a critical role in building an app that delivers value to users while achieving business objectives.
2. Stage 1: Ideation and Market Research
Every successful app begins with a solid idea backed by thorough market research.
2.1 Define Your App’s Purpose
Ask yourself:
- What problem does my app solve?
- Who is my target audience?
- What makes my app unique?
2.2 Conduct Market Research
Gather insights from competitors, analyze user needs, and identify gaps in existing solutions.
Tools for Research:
- Google Trends – Understand demand
- App Annie – Analyze competitors
- Statista – Track industry statistics
Example: Uber’s founders validated their idea by testing local demand for ride-sharing before scaling globally.
(Source: Statista App Economy Report 2025)
3. Stage 2: Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframes are the blueprint of your app — a visual guide that outlines the structure and functionality of each screen.
3.1 Create Wireframes
Wireframes define navigation, layout, and content hierarchy. They serve as the foundation for UI/UX design.
Tools: Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD
3.2 Build Prototypes
A prototype transforms wireframes into interactive, clickable designs to simulate user interactions.
Benefits:
- Helps visualize the final app flow
- Identifies usability issues early
- Facilitates stakeholder approval
3.3 Conduct Usability Testing
Test prototypes with real users to validate ease of navigation and intuitiveness.
Example: Airbnb used multiple prototype iterations to simplify its booking flow, improving conversion rates by 25%.
4. Stage 3: UI/UX Design — The User Experience Stage
An app’s design determines its first impression. A well-designed app enhances usability, engagement, and retention.
4.1 UI (User Interface) Design
Focus on color schemes, typography, and branding consistency. The design should be clean, intuitive, and aligned with platform guidelines.
Platform Guidelines:
- Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines
- Google’s Material Design Principles
4.2 UX (User Experience) Design
UX ensures smooth navigation and logical flow. Avoid clutter, minimize user steps, and ensure accessibility.
Pro Tip: Incorporate feedback loops early in the design phase to refine user journeys.
Stat: 75% of users judge app credibility by its design and ease of use (Forbes, 2025).
5. Stage 4: Development — Bringing Your App to Life
This phase involves converting the design into a working product using code.
5.1 Choose the Right Technology Stack
| Layer | Technologies |
|---|---|
| Frontend (Client-Side) | Swift, Kotlin, Flutter, React Native |
| Backend (Server-Side) | Node.js, Django, Firebase, .NET |
| Database | PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Firestore |
| Cloud Platforms | AWS, Google Cloud, Azure |
5.2 Frontend Development
Focus on creating a responsive and high-performance interface.
5.3 Backend Development
Handles data management, authentication, and server-side logic.
5.4 API Integration
Connect third-party services like payments, maps, or analytics.
Example: Spotify integrates APIs for music streaming, user authentication, and personalized playlists.
(Source: Google Developers Blog)
6. Stage 5: Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
Testing ensures your app is bug-free, secure, and performs seamlessly across devices.
6.1 Types of Testing
- Functional Testing: Verifies each feature works as intended
- Usability Testing: Ensures user-friendliness
- Performance Testing: Evaluates speed and stability
- Security Testing: Detects vulnerabilities
- Compatibility Testing: Checks performance on multiple OS versions
6.2 Testing Tools
- Appium
- TestFlight (for iOS)
- Firebase Test Lab
6.3 Beta Testing
Before public release, launch a beta version to gather feedback from real users.
Example: WhatsApp’s beta program identifies bugs before every global update, maintaining stability for billions of users.
7. Stage 6: Deployment and Launch
After testing, it’s time to release your app to the public.
7.1 App Store Preparation
Each app store has submission requirements and approval processes.
Apple App Store:
- Register for a developer account ($99/year)
- Follow App Store Review Guidelines
Google Play Store:
- One-time registration fee ($25)
- Follow Google Play Policies
7.2 App Store Optimization (ASO)
Optimize app listing with relevant keywords, attractive visuals, and engaging descriptions to boost visibility.
Checklist:
- App title with keywords
- Clear description
- High-quality screenshots and demo video
Example: Calm optimized its keywords around relaxation and meditation, resulting in a 30% increase in downloads.
8. Stage 7: Post-Launch Maintenance and Updates
An app’s journey doesn’t end at launch. Ongoing maintenance keeps your app relevant and competitive.
8.1 Monitor Performance
Use analytics tools to track user behavior and identify issues.
Tools: Google Analytics for Firebase, Mixpanel, AppDynamics
8.2 Regular Updates
Add new features, fix bugs, and improve performance based on feedback.
8.3 User Engagement
- Encourage reviews and ratings
- Implement loyalty rewards
- Send personalized push notifications
Example: Netflix releases updates weekly to improve streaming quality and add new personalization features.
9. Agile Development and Continuous Improvement
Agile methodology allows flexibility and faster releases by dividing development into smaller sprints.
Benefits of Agile:
- Continuous feedback integration
- Faster time-to-market
- Easy adaptation to changes
Pro Tip: Combine Agile with CI/CD pipelines for automated testing and deployment.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls to save time and ensure app success:
- Skipping market validation
- Overloading features in the MVP
- Ignoring security protocols
- Neglecting post-launch updates
Example: Apps that ignored user feedback had 40% higher churn rates (AppAnnie, 2025).
11. The Role of DevOps in App Development
DevOps bridges the gap between development and operations, enabling smoother deployments.
Key Practices:
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Continuous Delivery (CD)
- Automated Testing
Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI
Example: Uber’s DevOps automation allows weekly global updates with minimal downtime.
12. Cost and Timeline Breakdown
The cost of developing a mobile app depends on features, complexity, and platforms.
| App Type | Average Cost (USD) | Development Time |
|---|---|---|
| Simple App | $25,000 – $50,000 | 2–3 months |
| Medium Complexity | $50,000 – $120,000 | 4–6 months |
| Complex App | $120,000+ | 6–12 months |
(Source: Clutch Mobile App Development Survey 2025)
Tip: Outsourcing development to experienced offshore teams (e.g., India, Eastern Europe) can reduce costs by up to 60%.
13. Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Zoom
Zoom scaled from 10 million users to over 300 million during the pandemic by maintaining agile development and cloud infrastructure.
Case Study 2: Duolingo
Duolingo continuously refines features based on analytics and user behavior, helping it reach 600+ million users worldwide.
14. Final Thoughts: Building for Success
A well-executed mobile app development lifecycle ensures your app meets user needs, performs reliably, and scales for future growth.
To recap:
- Start with research and wireframes.
- Focus on clean design and performance.
- Test thoroughly before deployment.
- Commit to continuous improvement post-launch.
Success in app development isn’t just about building software—it’s about creating experiences that users love.
Call-to-Action: Build Your App with MobileMerit.com
Ready to turn your idea into a high-performance mobile app? Partner with MobileMerit.com — your trusted mobile app development company for Android and iOS.
We specialize in:
- End-to-End App Development
- Cross-Platform Solutions (Flutter / React Native)
- UI/UX Design & Prototyping
- Cloud Integration & App Maintenance
Contact us today for a free consultation and project estimate.
Visit MobileMerit.com — where your vision becomes a mobile reality.
